Althoughpreheating is something most of us first learned about in private pilot ground school, itremains a subject that’s poorly understood even by experienced pilots and aircraft owners.There are a lot of misconceptions about why preheating is important, when it’s necessary,and how it should be accomplished. But, by the time you’ve finished this article, Ipromise that you’ll be an expert on the subject.
Althoughpreheating is something most of us first learned about in private pilot ground school, itremains a subject that’s poorly understood even by experienced pilots and aircraft owners.There are a lot of misconceptions about why preheating is important, when it’s necessary,and how it should be accomplished. But, by the time you’ve finished this article, Ipromise that you’ll be an expert on the subject.
How cold is cold?
The first question that invariably comes up is how cold it has to be before preheatingis necessary. Of course, there’s no hard and fast answer to that question. The degree towhich a cold start will damage an engine depends on a variety of things, including thetype of engine, its age and condition, what sort of cylinders it has (steel vs. chrome),and what kind of oil is being used.
Interestingly enough, a brand new factory reman is considerably more vulnerable to coldstart damage than a tired old engine near TBO. Surprised? Stay tuned and you’ll find outwhy.
As a general rule, we consider any start in which the engine is cold-soaked to atemperature below freezing (32F or 0C) to be a “cold start,” and any startbelow about 20F (-7C) to be nothing short of a capital offense against yourpowerplant. The colder the temperature, the worse the crime.
Oil pressure isn’t enough!
Most pilots seem to think that the main reason cold starts are bad for engines is thatthe engine oil is thick and viscous and doesn’t flow well. Since it takes longer for oilpressure to come up when the oil is cold, the engine sustains excess wear in the earlyseconds after start because of inadequate lubrication. That’s what my primary CFI taughtme when I was studying for my private ticket 35 years ago.
That might have had some validity back then, but not today. Nearly everyone who fliesin cold weather nowadays uses multiviscosity oil such as Shell 15W-50 or Chevron 20W-50,and those oils flow extremely well even at 0F (-18C) or less.
Consequently, pilots who use multivis oils quickly observe that their oil pressurecomes up quickly after starting even in cold weather, and they figure that thereforeeverything’s okay. Big mistake!
Bearings need clearance…
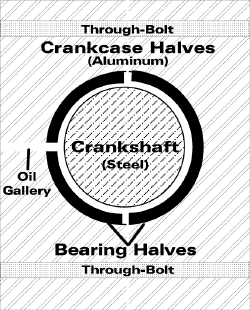 Crankshaft bearing clearance. |
The real culprit in cold-start damage is the fact that our aircraft engines are made ofdissimilar metals with radically different expansion coefficients. The crankcase, pistonsand cylinder heads of your engine are made from aluminum alloy, while the crankshaft,camshaft, connecting rods and cylinder barrels are made from steel. When heated, aluminumexpands about twice as much as steel. Likewise, when cooled, aluminum contracts abouttwice as much as steel. And, therein lies the problem.
Consider your steel crankshaft, which is suspended by thin bearing shells supported bya cast aluminum crankcase. As the engine gets colder, all of its parts shrink in size, butthe aluminum case shrinks twice as much as the steel crankshaft running through it. Theresult is that the colder the temperature, the smaller the clearance between the bearingshells and the crankshaft. That clearance is where the oil goes to lubricate the bearingsand prevent metal-to-metal contact. If there’s not enough clearance, then there’s no roomfor the oil, regardless how high the oil pressure gauge reads.
How significant is this problem. Well, take the TCM IO-520-series engines used in manyBeech and Cessna singles and twins, for example. The IO-520 overhaul manual lists theminimum crankshaft bearing clearance as 0.0018 inch (that’s 1.8 thousandths) at normalroom temperature.
What happens to that clearance when you start cooling the engine down? TCM doesn’t say.But tests performed in 1984 by Tanis Aircraft Servicesin Glenwood, Minn. (where it gets mighty cold) indicated that an IO-520 loses 0.002 inch(2.0 thousandths) of crankshaft bearing clearance at -20F. An engine built to TCM’sminimum specified bearing fit at room temperature would actually have negative bearingclearance at -20F-in other words, the crankshaft would be seized tight!
You’ve probably noticed how difficult it is to pull the prop through by hand beforestarting in cold weather. Now you know why. It’s not that the oil is thick (because if youuse multivis oil, it’s not). It’s that the clearance between the crankshaft and bearingsis tighter than normal. If it’s cold enough, you might not be able to pull the propthrough at all.
Start an engine in this condition and you’re likely to experience accelerated bearingwear and possible damage to the crankshaft journals in the first minute or two of engineoperation. If bearing clearances are small enough, it’s even possible for the bearingshells to shift in their saddles-a so-called “spun bearing-misaligning the oil feedholes and starving the bearing from lubricating oil.
Ironically, this problem is at its worst with a fresh-from-the-factory engine built tothe tightest new-engine tolerances. A tired, loose, high-time engine with worn bearings(or an engine with low time since a sloppy bargain-basement overhaul) might well haveplenty of clearance even at subzero temperatures.
But, even if your engine is approaching TBO, you can’t afford to be complacent aboutcold starts. That’s because inadequate bearing clearance is only one of several evilsassociated with cold starting.
…And pistons do, too
Consider what happens to your pistons and cylinders when you cold-start an engine.Here, the situation is the opposite of the one we just talked about: instead of a steelcrank inside an aluminum case, we have an aluminum piston inside of a steel cylinderbarrel. So the clearance situation is reversed: piston-to-cylinder fit is loose when theengine in cold, and tightens up as the engine comes up to full operating temperature.(This is why compression tests are normally done when the engine is hot.)
So why would cold starting be a problem for the engine’s top end? Several reasons.
When an engine is started cold and comes up to temperature, the piston and cylinderbarrel don’t warm up at the same rate. The piston heats up very rapidly after start, whilethe cylinder barrel may take quite a long time to warm up. Why? Well, for one thing, thepiston is small and light, while the cylinder his big and heavy, so when both are exposedto the heat of combustion, the piston heats up a great deal faster. In addition, thecylinder has a very effective mechanism for shedding heat-it’s covered with cooling finsbathed in what is presumably frigid air-while the piston’s only real cooling comes fromthe splash of engine oil, and the low RPMs of start and idle there’s not a whole lot ofsplash oil available.
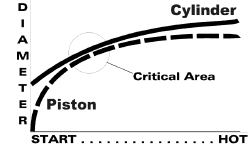 Piston-to-cylinder clearance. |
The result is that the piston expands to its full operating dimension quite quicklyafter start, while the cylinder takes a lot more time to expand to its full operatingdiameter. The colder the OAT, the longer it takes for the cylinder to reach operatingtemperature. The result is that although the fit of the piston in the cylinder is quiteloose when the engine is cold, it may quickly become tighter than normal shortly afterstarting when the piston has come up to temperature but the cylinder still has a long wayto go. If it’s cold enough, the piston-to-cylinder clearance can actually wind up going tozero, resulting in metal-to-metal scuffing between the piston and cylinder barrel.
This problem is made worse by the fact that most cylinder barrels are designed with ataper or “choke” in the top one-third of piston travel. This is done topre-compensate the barrel for the fact that, as the engine comes up to operatingtemperature, the top of the cylinder (where the combustion process takes place) is a lothotter than the bottom of the cylinder, and therefore expands considerably more. Ifcylinders were perfectly cylindrical at room temperature, then they’d become flared at thetop when the engine was hot, resulting in loose fit between the piston and cylinder barrelright where a tight fit is most needed-at top dead center. By giving the cylinder barrel aslight taper at the top when at room temperature, the cylinder winds up being cylindricalat operating temperature.
When an engine is started in cold weather, the cylinder choke starts out considerablygreater than normal. After start, the piston starts being repetitively forced up into thechoked-down area at the top of the stroke. As the piston quickly comes up to temperaturebut the cylinder is still relatively cold, it’s easy to see how severe scuffing can occurat the top of stroke.
As you can see from this discussion, warming up the engine oil is definitely not enoughto avoid cold-start damage. All the warm oil in the world won’t help if thecrank-to-bearing or piston-to-cylinder clearances go to zero. To avoid this, it’sessential for a preheat to warm up the crankcase and the cylinder barrels (especially thetop of the cylinder barrels near where they mate to the heads).
The world’s finest preheat
The best way to accomplish this is to put the airplane in a heated hangar overnight.Why? Because this preheats every part of the airplane to an even temperature. After 8 to12 hours in a 40F hangar, the oil is at 40F, the case is at 40F, the cylinder headsare at 40F, the gyro instruments are at 40F (gyros have their own cold-startingproblems, by the way), the windshield is at 40F (so it won’t fog up the minute youexhale), and even the pilot’s seat is as 40F (which solves another problem).
I’m based on the California coast where the weather hardly ever gets below freezing,but when I travel to the cold country, I always try my best to use theovernight-in-a-heated-hangar method of preheating. Most FBOs seem to charge anywherebetween $20 and $50 to store my 310 in their heated hangar overnight. Even at $50, Ifigure it’s quite a bargain compared to the alternative (accelerated wear of my twoexpensive TSIO-520 engines).
If I’ll be staying at a cold-weather airport for awhile, I’m often too much of askinflint to pay for the airplane to be hangared for the whole duration. Instead, I’llarrange with the FBO to pull the airplane into the heated hangar the night before myscheduled departure. If it’s really, really cold out on the morning of departure, I’vebeen known to preflight the airplane in the hangar, climb into the cockpit, secure thedoor, and then have the line crew open the hangar door and tow the airplane out onto theramp with me in it. As soon as they unhook the tug, I start the engines before they’ve hada chance to get cold-soaked.
Multipoint electric heaters
Short of overnight in a heated hangar, the best preheating method is a multipointelectric heating system that has individual heating elements attached to the oil pan, thecrankcase, and each cylinder. By plugging such a system into 115V or 230V power a fewhours before departure (overnight is even better), you can at least be assured of warmcylinders, a warm case, and warm oil when you start up.
 Tanis TAS100 system. |
The best-known multipoint electric preheating systems come from Tanis Aircraft Services in Glenwood, Minn. The TanisTAS100-series systems cost about $500 for a six-cylinder engine and consist of eightelectric heating elements connected by a wiring harness. Six 50-watt cylinder heatersscrew into the threaded CHT-probe bosses in each cylinder head. A flat silicone rubberheating pad is glued to the crankcase with high-temp RTV, and another is glued to thebottom of the oil pan. The wiring harness terminates at an ordinary AC plug that isusually mounted near the oil filler door in the cowling. You simply run an extension cordout to the airplane, plug in the preheating system, and let it cook for a few hours.
Although the Tanis TAS100 is a terrific preheating system, one drawback is that itscylinder heaters displace the normal CHT probe. One solution is to change to aspark-plug-gasket-type CHT probe. Another is to use a combined heater/probe elementavailable from Tanis, but this makes the system more expensive, particularly if you haveprobe-per-cylinder EGT/CHT instrumentation such as a GEM or JPI 700.
 Reiff HOTBANDD system. |
In 1992, Reiff Corporation of Delafield,Wisc. entered the multipoint electric preheating market with their novel”HOTBANDD” system. In lieu of cylinder head heaters, the Reiff system uses50-watt heating elements mounted on large stainless steel clamps that mount on thenon-finned portion of each cylinder barrel. As a result, there’s no interference withexisting CHT instrumentation. The Reiff system also includes an oil pan heater, but not acrankcase heater (the theory presumably being that the crankcase receives sufficient heatby conduction from the oil pan and cylinder heaters). A six-cylinder Reiff system sellsfor about $400.
 Tanis TAS400 heated rocker gaskets. |
Not to be outdone, Tanis recently came out with anew TAS400 preheating system. In lieu of the CHT-boss heating elements, the new systemuses a “heated rocker gasket” which fits between each cylinder head and rockercover, and applies heat directly to the cylinder head. The TAS400 is a significantimprovement over the TAS100 system in a couple of different ways. Not only does it solvethe CHT-probe interference problem, but it also applies heat evenly to the fullcircumference of the cylinder head, rather than applying it all at a single point.
Both the new Tanis TAS400 system and theReiff HOTBANDD system are capable of providing anexcellent preheat in a couple of hours. We do not recommend cheaper electric systems thatheat only the oil pan. As you now know, heating the cylinders and case is absolutelyessential.
Engine and prop covers
 Insulated engine and prop covers by Kennon Aircraft Covers. |
If the temperature is not too frigid and the aircraft is being preheated in atee-hangar or other protected area, then a multipoint electric heating system is all youneed to do the job. But if it’s really cold, or if you have to preheat outside on anexposed ramp (particularly if it’s windy), then you also need some means of insulating theengine compartment and keeping most of the heat from escaping.
At the very minimum, you’ll need an insulated engine cover. Although you may be able tomake do with a quilted blanket, custom-fitted insulated covers are available fromKennon Aircraft Covers in Sheridan, Wyo., as well as from bothReiff and Tanisand a few other firms.
In intense cold or windy conditions, the propeller becomes a major source of heat lossduring preheating. Kennon,Reiff and Tanisall offer insulated propeller and spinner covers to solve this problem. Figure about $300for a good insulated engine cover, and $100 more to cover the prop and spinner.
Another compelling advantage of insulated engine and prop covers is that using them mayeliminate the need for a preheat altogether if you’re going to be making a quick-turn. Byinstalling the covers promptly after shutting down, engine heat can be retained for threeor four hours even when the airplane is parked outside on a cold, windy tiedown.
Other electric heaters
If you hangar your airplane and use an insulated engine cover, a single-point electricheater can provide an adequate preheat if it is given enough time to do so (e.g.,overnight). A simple oil pan heater can do the trick, and even a couple of 100-watt lightbulbs stuck up the cowl flaps may suffice if the engine compartment is well covered.
Kennon offers a novel variation on this theme, consisting of a pair of electricallyheated plates velcroed to the inside of cowl plugs. Combined with a good insulated enginecover and possibly an oil sump heater, this can do a good job of keeping the engine warmin all but the most frigid conditions.
These approaches work fine so long as you have plenty of time to preheat, but don’texpect them to heat a cold-soaked engine to safe starting temperature in an hour or two.For that, you’ll definitely need a multipoint electrical heating system, or a forced-airpreheat.
Leave it on all the time?
There has been considerable controversy about whether or not it’s a good idea to leavean electric preheating system plugged in continuously when the airplane isn’t flying. BothTCM and Shell have published warnings against leaving engine-mounted electric preheaterson for more than 24 hours prior to flight. However, these cautions are really applicableprimarily to single-point heaters such as oil pan heaters.
The concern of TCM and Shell is that heating the oil pan will cause moisture toevaporate from the oil sump and then condense on cool engine components such as thecamshaft, crankshaft or cylinder walls, resulting in accelerated corrosion of those parts.However, if the entire engine is heated uniformly by means of a multipoint heating system,or because the engine and propeller are covered with insulated engine and prop covers,such condensation is very unlikely to occur.
In fact, using an insulated cover and a multipoint preheating system that is plugged incontinuously is one of the most effective methods of eliminating internal enginecorrosion, particularly if the aircraft is kept in an unheated hangar rather thanoutdoors. If the entire engine is maintained above the dewpoint, condensation simplycannot occur.
Forced hot air
 Herman-Nelson forced-air preheater. |
Most FBOs in the cold country use large forced-air preheating units like thosemanufactured by Aerotech-Herman-Nelson inWinnipeg, Canada. Smaller hot air heaters fired by propane, kerosene or gasoline are alsoavailable from a number of sources, including Kennon AircraftCovers.
Forced-air preheating can do an effective job, provided the machine has sufficient BTUoutput for the job (some small propane-fired heaters simply don’t), and the machine isleft hooked to the airplane for enough time to heat the engine thoroughly. Unfortunately,if you’re depending on an FBO for a hot-air preheat one chilly morning, chances are abunch of other pilots are, too. Unless the FBO is willing to devote sufficient time topreheating your aircraft (and how long that is depends on both the capacity of the heaterand the OAT), you may wind up with a partially-heated engine that has hot spots and coldspots.
How can you tell whether you’ve received an adequate preheat? It’s not easy, but if youcan manage to get your hand inside the engine compartment and if all the rocker covers andthe crankcase feel warm to the touch, you’re probably okay.